|
ARPAnno - HELP and Supplementary information |
The Multiple Alignment of Complete Sequences of all ARPs is available here.
1- Program overview
2- Actin superfamily a specific family of proteins
3- ARPAnno process
4- How to use ARPAnno
5- Analysis
1- Program overview
Recent efforts in
high-throughput sequencing have given rise to a rapid
increase in the amount of sequences available in the public databases.
Systematic characterization and annotation of this data is typically
performed by the Gene
Ontology (GO), a hierarchical and standardized
vocabulary developed by the GO
Consortium.
This automatic annotation has some limitations whith highly conserved
and widely distributed families of proteins. The actin superfamily is
one of theses families which share, for 546 conventional actin
sequences ranging 313 different organims, > 85 % identity among
their complete
length. Together with conventional actin, the Actin Related Families
(ARPs) are difficult to distinguish. We propose on the basis of a
complete sequence analysis of the ARP families, ARPAnno
a new web tool to automatically annotate the new actin-like sequences
and the Multiple
Alignments of Complete Sequences (MACS) of
all ARPs available in Uniprot (July 2004). The originality of the
method lies in
the determination of Insertion/Deletions signatures and specific
residues signatures to assess the annotation of the query
sequence.
2-
Actin superfamily a specific family of proteins
Due to high
sequence identity and
similarity between ARPs and actin sequences, it is frequently difficult
to unambiguously detect and classify ARP sequences from BlastP
databases
searches. Indeed the Blast score and ranking of ARP homologous
sequences is
perturbed by the presence of insertions and deletions (INDELs) and the
existence of
a very limited number of discriminating residues (see material and
methods).
As an example, the search of homologues (BlastP) for the human ARP1 in
Uniprot leads to 1653 protein
“hits” exhibiting a significant E-value (E≥10-3).
Among these 1653 proteins, ARP1 sequences are dispersed among
conventional actin and other ARPs. The last ARP1 detected was the yeast
ARP1 at rank 769, lower than many non ARP1 sequences. This prompted us
to better define
discriminating criteria for each family using specific residues as well
as specific insertions and deletions.
3- ARPAnno process
The Actin
Related Proteins Annotation
server (ARPAnno)
is written in Tcl/Tk script and has 3 main steps.
i) First ARPAnno aligns the query sequence with BlastP against dedicated databases of each subfamily contained in ARP-MACS (orphans, actin and 11 ARP subfamilies). Eligible subfamilies which are the most suitable to continue any further investigation are then determined by the calculation of 2 cut-offs:
- GID is a global percent identity computed as the ratio of the number of identical residues to the number of residues of the query in all aligned fragments of the comparison or HSPs (High Scoring Pairs).
- pCover is a percent covering expressed as the ratio of the number of identical residues to the number of residues that could be aligned between the 2 sequences.
These 2 cut-offs provide an enhanced filter of the blasts search to select and rank the ARP families.
ii) In a second step the query is aligned against the MACS from the eligible families by the clustalw program in profile mode and filtered using the residues and INDELs signatures. For each family tested, the filter calculates 2 new cut-offs:
- pDI is the number of discriminating insertions detected as a percentage of the total number of discriminating insertions characterized for the considered ARP family.
- pDR is the number of discriminating residues detected for the query as a percentage of the total number of residues and motifs described for the considered ARP family.
iii) In the last step, a final score on a scale of 0 to 100 is computed for each subfamily based on the local and global alignment and the knowledge-based filters. The relative weights of each score were determined experimentally to best separate the subfamilies.
i) First ARPAnno aligns the query sequence with BlastP against dedicated databases of each subfamily contained in ARP-MACS (orphans, actin and 11 ARP subfamilies). Eligible subfamilies which are the most suitable to continue any further investigation are then determined by the calculation of 2 cut-offs:
- GID is a global percent identity computed as the ratio of the number of identical residues to the number of residues of the query in all aligned fragments of the comparison or HSPs (High Scoring Pairs).
- pCover is a percent covering expressed as the ratio of the number of identical residues to the number of residues that could be aligned between the 2 sequences.
These 2 cut-offs provide an enhanced filter of the blasts search to select and rank the ARP families.
ii) In a second step the query is aligned against the MACS from the eligible families by the clustalw program in profile mode and filtered using the residues and INDELs signatures. For each family tested, the filter calculates 2 new cut-offs:
- pDI is the number of discriminating insertions detected as a percentage of the total number of discriminating insertions characterized for the considered ARP family.
Ex: ARP8 family has
4 specific insertions. If the query protein has 3
of them it will have a pDI of 75% (3/4).
- pDR is the number of discriminating residues detected for the query as a percentage of the total number of residues and motifs described for the considered ARP family.
Ex: ARP2 family has
6 group of specific residues. If the query protein
has 3 of them it will have a pDR of 50% (3/6).
iii) In the last step, a final score on a scale of 0 to 100 is computed for each subfamily based on the local and global alignment and the knowledge-based filters. The relative weights of each score were determined experimentally to best separate the subfamilies.
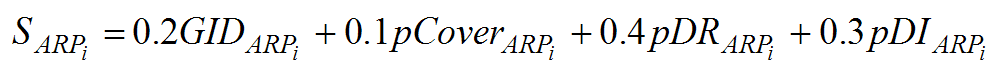
4- How to use ARPAnno
The main page of ARPAnno
allows you to run the program with a new sequence (paste a
sequence in FASTA
format) or to retrieve an existing session (session ID, see
below).
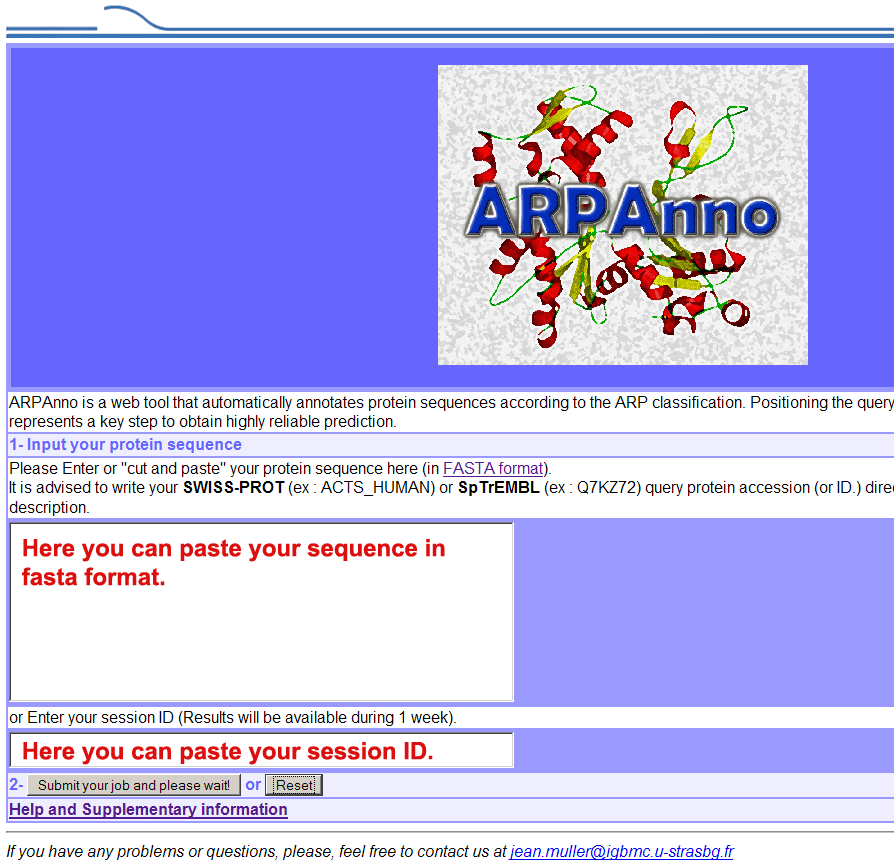
You can
submit your job by clicking on the button below (Submit
your job and please wait). The next page will give you an "session
ID" (ex: 1234_2784_3421) while you wait for the end of the
job.
This session ID can be used to retrieve an existing job, either completed or ongoing (e.g. if you have no time to follow it or if you want to consult it later).
This session ID can be used to retrieve an existing job, either completed or ongoing (e.g. if you have no time to follow it or if you want to consult it later).

When the job is
finished, the result page will be available trough a
new link in the same page.

If your protein is
close enough to actin and ARP proteins, it will be analysed, otherwise
a message is prompted.
The result are displayed in a table with families in rows and the 5 scores in columns. The blue column highlight the final score. The best family is highlighted in orange.
The result are displayed in a table with families in rows and the 5 scores in columns. The blue column highlight the final score. The best family is highlighted in orange.
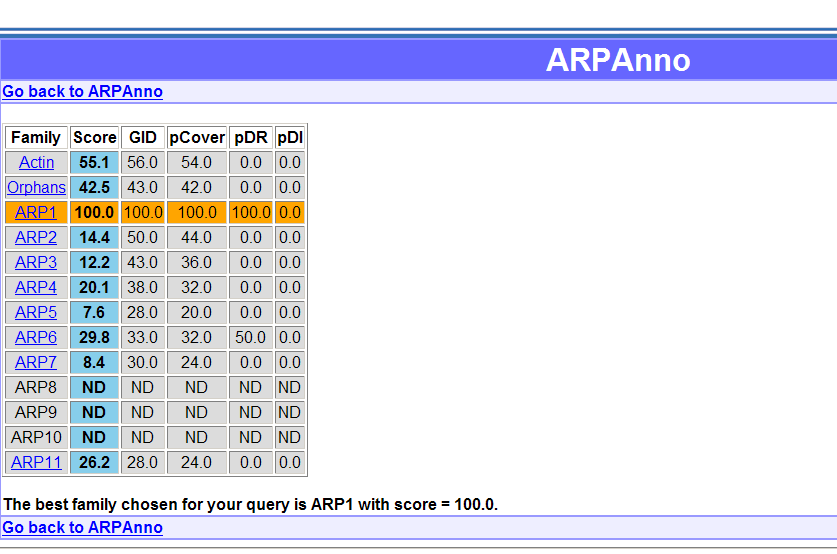
By clicking on the
name of the families you will access to blast
results or annotated multiple alignment. The multiple alignment is
shown with the specific residues and insertions differentially colored.
When visualizing multiple alignments, you can maintain your mouse
cursor on each features
to see additional informations (relative and absolute positions,
residue
value). Your sequence is noted as "query_protein", and besides all ARP
proteins we also add one conventional actin (our reference actin) named
P02568. You can also click on each accession numbers to gain access
directly to the corresponding entry in Uniprot database using SRS (Sequence Retrieval
Software) program.
Ex 1:
ARP1 family results. The first specific motif is displayed in orange
and a
small help bubble, obtained by passing your mouse over specific
features, gives you information such as position, size...
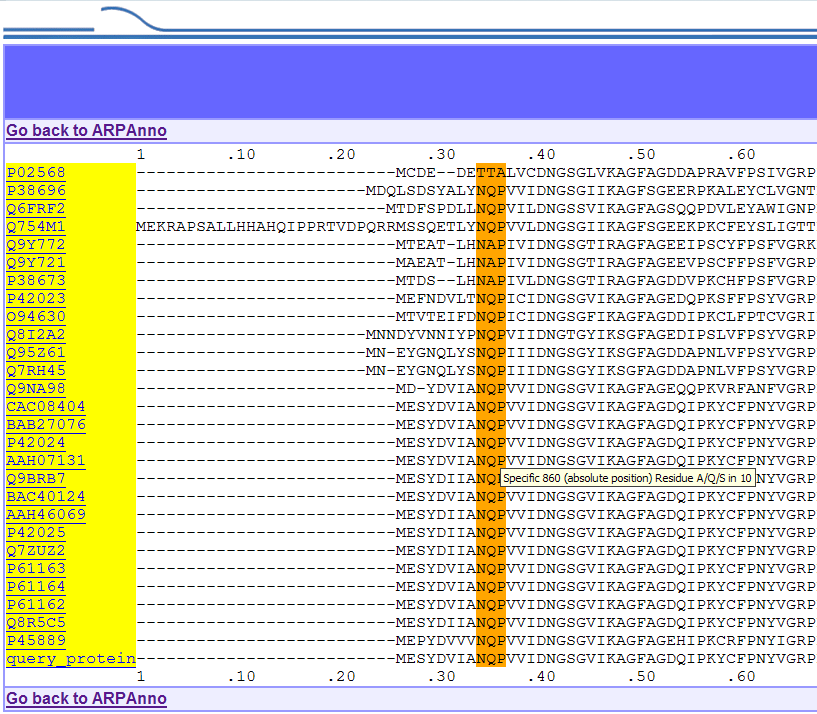
Ex 2:
ARP3 family results. The partial MACS shows 2 specific motifs and
residues coloured in blue and purple respectively, and 1 insertion
coloured in pink.

5- Analysis
In order to
estimate the accuracy and reliability of the ARPAnno annotations, we
submitted each of the ~700 previously identified actin and ARP proteins
in ARP-MACS for automatic
classification. In this large-scale test, all proteins were assigned to
the correct subfamilies. To evaluate the predictive strength of our
server, we performed a second test involving the newly detected
proteins from the latest version of Uniprot. The second set was
composed of 68 sequences that were classified by the
program with best Score ranging from 36.9 to 99.0
as follows; 36 conventional actin, 3 Orphans, 6 ARP1, 7 ARP2, 6 ARP3, 8
ARP4, 1 ARP9 and 1 ARP10 from
diverse organisms such as Y. lipolytica,
D. hansenii, Caenorhabditis
briggsae, Paramecium tetraurelia,
Xenopus tropicalis or Gallus gallus. According to our analysis
a Score > 55 is highly reliable for complete
sequences. Further validation by visual
inspection suggested that the only 2 sequences with Score
<
55 corresponded to 2 P. tetraurelia, classified as
actin subfamily
and annotated as putative actin in Uniprot.
We therefore recommend users to consider only best scores and to be aware that ambiguous situations can often be clarified by direct comparison to the MACS of the closest subfamilies.
We therefore recommend users to consider only best scores and to be aware that ambiguous situations can often be clarified by direct comparison to the MACS of the closest subfamilies.